Have you ever settled into your car seat and wondered about the intricate process behind its comfort and support? Indeed, the automotive seat manufacturing process is a sophisticated symphony of engineering, materials science, and precision assembly. Far from being a simple piece of furniture, a modern car seat is a critical safety component and a product of complex seat production. This guide will walk you through the entire journey, revealing the expertise required at each stage to create the seats that are fundamental to every vehicle.
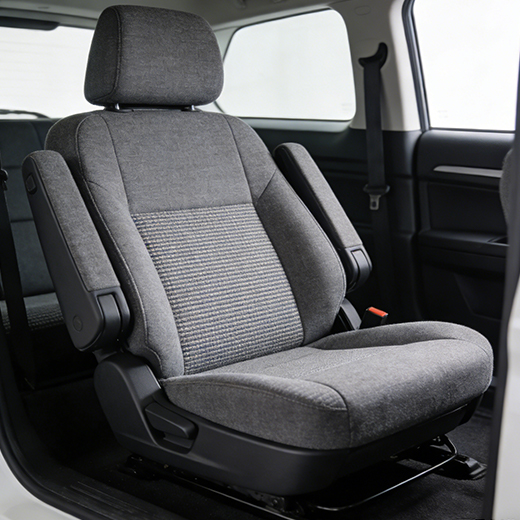

The Three Foundational Pillars of Car Seat Construction
Every automotive seat production begins with three core components that define its safety, comfort, and aesthetics. These elements are manufactured in parallel before converging in final assembly.
The Frame: The Structural Backbone of Seat Manufacturing
The seat frame is the foundation, engineered for strength and safety. Its creation involves precision metal stamping and fabrication processes. Manufacturers use advanced techniques to shape high-strength metals into components that are then robotically welded. Consequently, this frame must be incredibly durable to withstand crash forces, yet lightweight to contribute to overall vehicle efficiency, showcasing the balance struck in modern auto seat production.
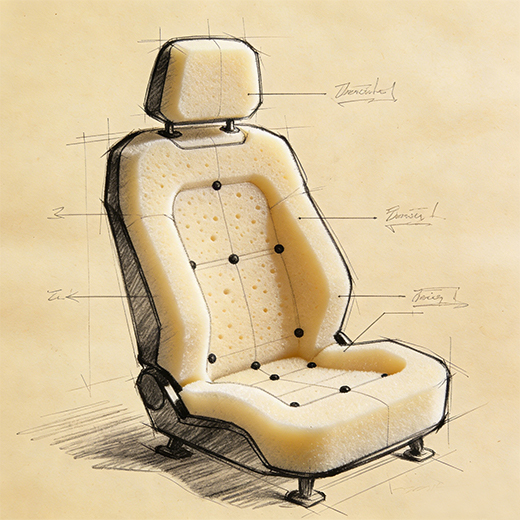
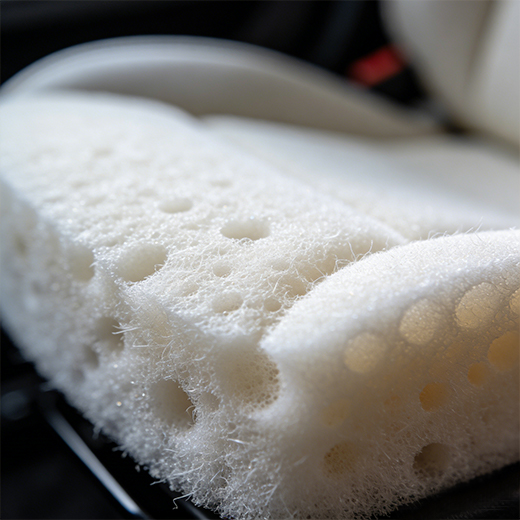
The Foam: Engineered Comfort through Advanced Molding
The comfort you feel is the result of advanced materials engineering. In a specialized foam molding process, liquid polyurethane is poured into precise molds, where it expands and cures into shape within minutes. This process doesn’t just create padding; it forms specific contours, trenches, and channels that are crucial for both comfort and the integration of fastening systems during later seat assembly stages.


The Trim Cover: Where Design Meets Manufacturing Precision
The visible surface of the seat is a feat of textile and manufacturing engineering. Trim covers are cut from durable, tested fabrics and synthetics, then assembled by skilled technicians and automated sewing systems. They are more than just aesthetics; these covers must resist years of wear, UV exposure, and stains. Furthermore, they are manufactured with integrated attachment points for the complex fastening systems that ensure a flawless, secure fit.



The Synchronized Four-Step Seat Production Process
The automotive seat manufacturing process follows a meticulously planned sequence to ensure efficiency, quality, and integration with vehicle assembly lines.
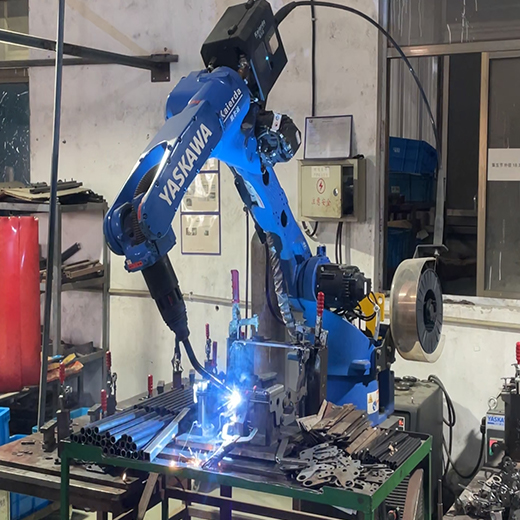
Step 1: Precision Frame Fabrication and Assembly
The manufacturing journey begins by transforming raw metal into the seat’s skeleton. Using cutting-edge metal stamping, bending, and robotic welding, manufacturers first form and then join the individual metal components. This stage demands extreme precision; therefore, the finished frame must undergo rigorous validation to meet strict automotive safety standards before it can proceed to the next phase of the production line.

Step 2: Foam Molding and Curing
Simultaneously, specialized facilities produce the foam, often located near final assembly plants to optimize logistics. In this step, workers inject liquid foam components into molds that define the seat’s contour. After a short curing cycle, they remove the finished foam pad, which now contains integrated trenches designed to house fastening components—this step is a critical preparation for the upcoming trim and assembly phase.
Step 3: Trim Cover Manufacturing and Preparation
Running in parallel, the process also creates the trim cover. Here, computer-guided systems accurately cut rolls of material into panels. Next, skilled technicians or automated machines stitch these panels together to create the finished cover. Finally, they sew or attach sophisticated fasteners, like specialized hooks or clips, into precisely defined positions on the cover’s underside, which efficiently prepares it for the final installation.
Step 4: Final Assembly and Integration
At this final stage, all components converge at the Final Assembly Line, which is typically a “Just-in-Time” (JIT) facility located extremely close to the vehicle assembly plant. Here, the seat assembly process reaches its peak through a precise sequence of operations:
First, workers or automated systems securely attach the molded foam to the metal frame.
Next, they carefully stretch and fit the trim cover over the contoured foam.
Finally, they engage the hidden fastening systems—such as hooks, clips, and retainers—which lock the cover tightly into place to create crisp, professional seams and contours.
Following these assembly steps and a final comprehensive quality inspection, the facility immediately sequences and ships the completed seat to the vehicle assembly line, often within hours.
The Hidden Heroes: Fastening Systems and Quality Assurance
What truly brings a seat together are the often-unseen fastening systems. Modern automotive seat production relies on engineered solutions like:
- Advanced Hook-and-Loop: Specially designed strips molded into the foam that grip corresponding loops sewn into the trim cover.
- Precision Clip Systems: Plastic clips attached to suspenders on the cover that snap onto wires molded within the foam.
- Specialized Retainers and Zippers: Heavy-duty closures that secure different sections of the trim with strength and a seamless appearance.
Throughout the entire seat manufacturing process, manufacturers implement rigorous quality assurance protocols. Specifically, they control each step, from testing raw material durability and validating welded frame strength to performing final seat functionality checks. Furthermore, to ensure this consistent control, modern manufacturing facilities operate under international quality management standards like ISO 9001. Therefore, every seat that leaves the production line reliably meets the exacting specifications for safety, comfort, and appearance.
The Future and Importance of Expert Manufacturing
As vehicles evolve with electrification and autonomous driving, the field of automotive seat manufacturing actively adapts. Consequently, seats now integrate more electronics, which in turn requires new materials and refined assembly techniques. Furthermore, the production process itself is becoming smarter, leveraging increased automation and data analytics to enable predictive quality control.
This growing complexity underscores the immense value of specialized expertise. Specifically, successful auto seat production relies on deep knowledge spanning precision metalwork, polymer chemistry, textile engineering, and lean assembly logistics. Ultimately, this entire process demonstrates how multiple, specialized streams of manufacturing and engineering converge to create a single, essential component of your daily drive.